Tutorial
Transformations are the engine room of a workflow. They’re the step where raw input turns into something structured, enriched, or customized for your needs. Without transformations, workflows would just move data around as-is: useful, but limited. With transformations, you can clean, enrich, and reshape data on the fly. Here’s how they work.
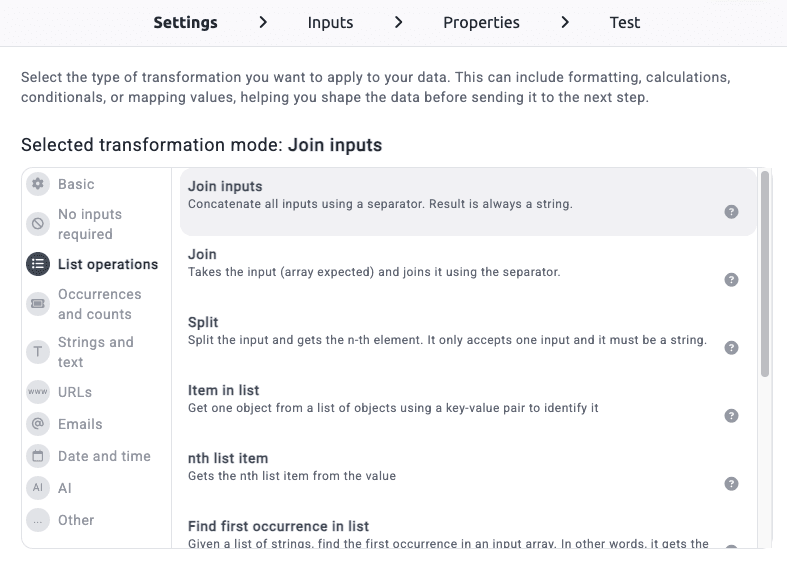
1. Choose the transformation mode
The first step in creating a transformation is selecting the mode.
The mode defines what operation should be applied to your data. There are many pre-built transformations available, each grouped by category and designed for a specific purpose. Most come with a small example (just click the question mark icon) so you can quickly see how they behave.
Some transformations work immediately with no setup, while others require additional configuration, such as specifying a rule, setting parameters, or writing an AI prompt.
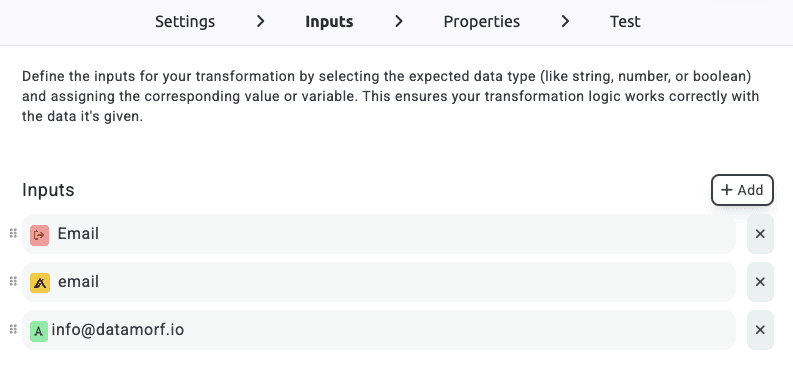
2. Define the inputs
Once you’ve picked a mode, the next step is telling the transformation what data to work with.
Think of a transformation like a factory: one or more ingredients go in, and one final product comes out.
Inputs are the data points you select to feed into the transformation. For example, if your trigger data contains an email address, you can point the transformation input to that value.
Some transformations require just one input, while others can accept multiple.
If you provide multiple inputs to a single-input transformation, it will automatically use the first non-empty value in your list.
This makes it easy to build fallback logic: “use value X, but if empty use value Y, and if that’s empty use value Z.”
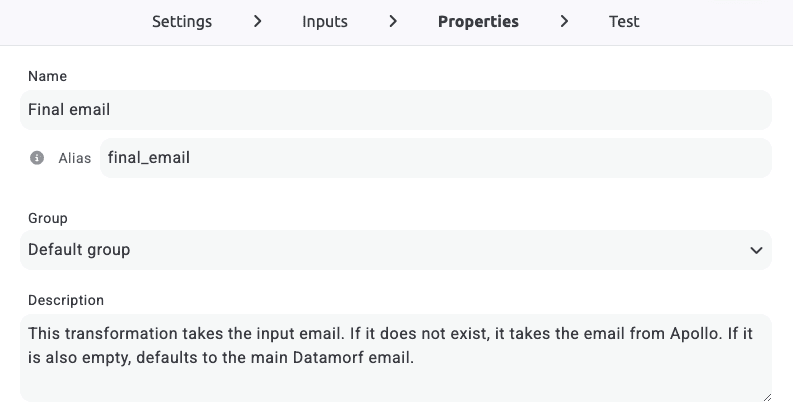
3. Add a clear name
Every transformation should have a readable name. This helps you, your teammates, and even your future self quickly understand what it does without having to open it up.
It may sound like a small detail, but naming transformations well saves a lot of confusion when building complex workflows.
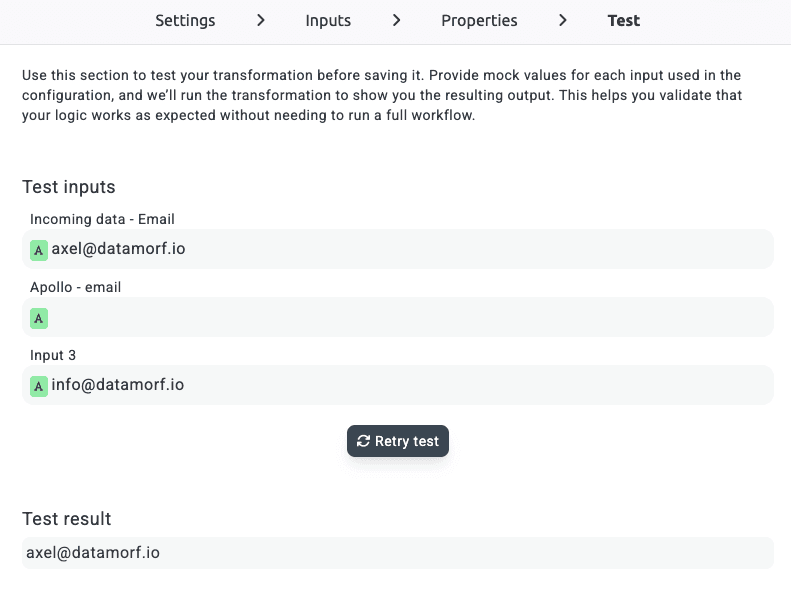
4. Test the Transformation
The final step is testing. Here you can provide mock data for the inputs you’ve defined, run the transformation, and immediately see the output.
This is especially powerful when working with AI-based transformations. You can iterate quickly by adjusting prompts, tweaking variables, and running tests until you’re confident the output is exactly what you need.
Building Complex Chains
Once you’ve built your first transformation, you can start chaining them together. The output of one can serve as the input of the next, creating layered transformations that handle even the most complex data processing needs.
From cleaning and normalizing values to generating personalized content with AI, transformations are what make workflows truly flexible and powerful.
Remember
A transformation follows four simple steps:
Choose a mode → Define inputs → Add a name → Test the output.
Master these steps, and you’ll unlock the ability to take any piece of data and shape it exactly how your workflow needs it.
PS: All transformations modes:
Basic
Default: Select as many inputs as needed. If the first one exists it will be the result. If it doesn’t we check the next one.
Maximum: Get the maximum value from the input list.
Minimum: Get the minimum value from the input list.
Comparison: Compare an input with a value and return a boolean.
Dot notation path: Tries to access a dot notation path on a given value.
No-inputs
Create random ID: Creates a random id using letters and numbers.
Execution ID: Gets the DataMorf workflow execution id.
Stop execution: Stops the workflow execution.
Arrays
Join inputs: Concatenate all inputs using a separator.
Join: Takes an array input and joins it using a separator.
Split: Split the input string and return the n-th element.
Item in list: Get one object from a list using a key-value pair.
nth list item: Gets the nth item in a list.
Find first occurrence in list: Given a list of strings find the first white-listed element in an array.
Sort list: Sort a list and return either the sorted list or a specific item.
Make list with inputs: Creates an array where each input becomes an item.
Extract property from array of objects: Extract a property from every element in a list.
Random selection: Randomly select one element from all inputs with equal chance.
Occurrences
Most frequent: Get the value that appears more times in the inputs.
Least frequent: Get the value that appears fewer times in the inputs.
Get size: Count how many items are in a list or object or how many characters in a string.
Strings
Stringify: Convert the input to a string.
to lowercase: Convert string to lowercase.
To UPPER case: Convert string to uppercase.
To Title Case: Convert string to title case.
To snake_case: Convert string to snake case.
To kebab-case: Convert string to kebab case.
To camelCase: Convert string to camel case.
Wrap string: Wrap a string with characters on both sides.
Search string: Search for a value inside a string. Supports regex.
Replace string: Replace a specific value inside a string. Supports regex.
Clean Html tags: Extract the plain text from HTML content.
Free text: Write text with embedded transformations.
Rich text: Same but supports rich text formatting.
JSON parse: Parse a JSON string into a JSON object.
Regex match: Match a string with a regular expression.
Urls
Extract URL parameter: Extract a parameter value from a URL.
Encode URL: Encode a URL using encodeURI.
Decode URL: Decode a URL using decodeURI.
Get domain name: Extract the domain from a URL.
Get top level domain: Extract the domain extension.
Get second level domain: Extract the domain without its extension.
Get host name: Extract host name from URL.
Is domain valid?: Returns true if the input is formatted as a valid domain.
Emails
Extract domain from an email: Get the email domain.
Extract name from an email: Get the email name.
Is email valid?: Returns true if the input is a valid email.
DateAndTime
Get date: Get a formatted date string. Defaults to now if no input.
Add date: Add hours days or weeks to a date.
Format date: Apply a specific date format.
Ai
GPT Prompt (old): Create a prompt and send to GPT using the old API.
GPT Prompt: Create a prompt and send to GPT using the new responses API.
Claude AI Prompt: Create a prompt and send it to Claude.
Prompt Layer: Run a PromptLayer template.
Name normalizer: Normalize company names person names and job titles with AI.
Perplexity: Create a prompt and send it to Perplexity models.
Other
Dictionary (switch case): Compare input value with key and return its mapped value.
Custom code: Write your own JS code.
Custom transformation: Run a pre-defined custom transformation.
Share
