Tutorial
Reverse ETL has become an essential part of modern data operations. Below is a clear breakdown of what reverse ETL is, how it differs from traditional ETL and why it matters for GTM teams.
1. What is Reverse ETL?
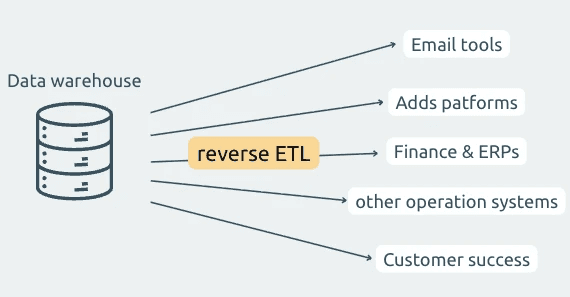
Reverse ETL is the process of retrieving data from external platforms (CRMs, databases, SaaS tools, spreadsheets, APIs, etc.) and syncing it back into your own systems or automations.
Instead of waiting for those systems to push events to you, reverse ETL lets you proactively fetch the data you need on a recurring schedule.
The goals of reverse ETL are:
keeping operational tools synchronized
ensuring teams work with the latest information
eliminating manual exports, scripts, and CSV uploads
automating cross-system consistency
Reverse ETL acts as the “inbound counterpart” of the traditional data pipeline.
2. Difference between ETL and Reverse ETL
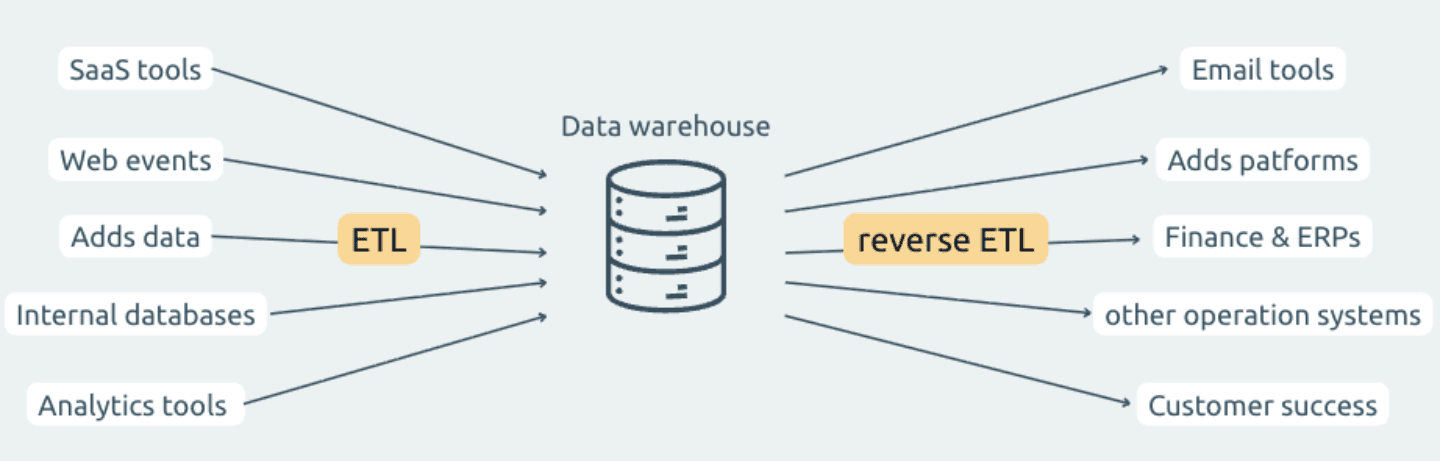
ETL and reverse ETL both move and transform data, but their direction and purpose are different:
Traditional ETL (Extract → Transform → Load)
Extracts data from operational systems
Loads it into a data warehouse or internal system
⇒ Used for analytics, BI, reporting, and long-term storage
Reverse ETL
Extracts data from SaaS tools or external systems
Sends it back to operational or workflow systems
⇒ Used for activation, enrichment, syncing, and automation
ETL is about analytics; reverse ETL is about operations.
3. How Reverse ETL is useful for GTM teams
Go-to-market teams increasingly rely on multiple SaaS tools: CRMs, analytics platforms, ad platforms, marketing automation systems, billing tools, and customer data stores. While all these tools are valuable individually, the real power emerges when they operate using the same, unified, up-to-date data.
Reverse ETL makes this possible by pulling data from key systems and sending it into the operational tools that GTM teams use every day.
Below are the detailed reasons why GTM teams benefit from Reverse ETL:
Aligns customer data across all GTM tools
Reduces manual data work
Enables better targeting and segmentation (Marketing)
Improves lead routing and conversion (Sales)
Strengthens cross-functional alignment (Revenue & Ops)
Unlocks real “lifecycle automation”
Improves attribution and reporting
Turns GTM data into action, not storage
Reverse ETL brings operational data directly to the tools that Sales, Marketing, and Ops use every day. Below are common use cases:
Marketing teams
Audience refinement: Pull CRM segments daily and sync them into ad platforms.
Lead enrichment: Fetch updated lead attributes and run them through automated scoring workflows.
Sales teams
Pipeline freshness: Sync opportunity changes into internal dashboards or sales enablement tools.
Data hygiene: Regularly fetch stale or missing fields and process them for cleaning.
Operations teams
Inventory or product syncs: Pull product data from databases and update operational systems.
Billing or subscription alignment: Retrieve billing platform data and reconcile with internal tools.
For GTM teams, reverse ETL ensures that every tool has the right data at the right time, without manual effort.
4. The Extractor feature in Datamorf
Datamorf includes a dedicated reverse ETL module called the Extractor.
It provides a structured way to:
run on a schedule,
fetch data from external SaaS tools, databases, APIs, or spreadsheets,
and inject each record (or batch) into a Datamorf workflow for further transformations.
The Extractor is tightly integrated with Datamorf’s automation engine, which means all incoming records can immediately go through transformations, AI enrichment, conditional logic, and multi-destination loading.
It eliminates the need for cron jobs, custom scripts, or manual exports.
5. How to set it up in Datamorf
The Extractor in Datamorf is similarly structured as the workflow architecture which makes it even easier to master. Every extraction follows the same three steps.
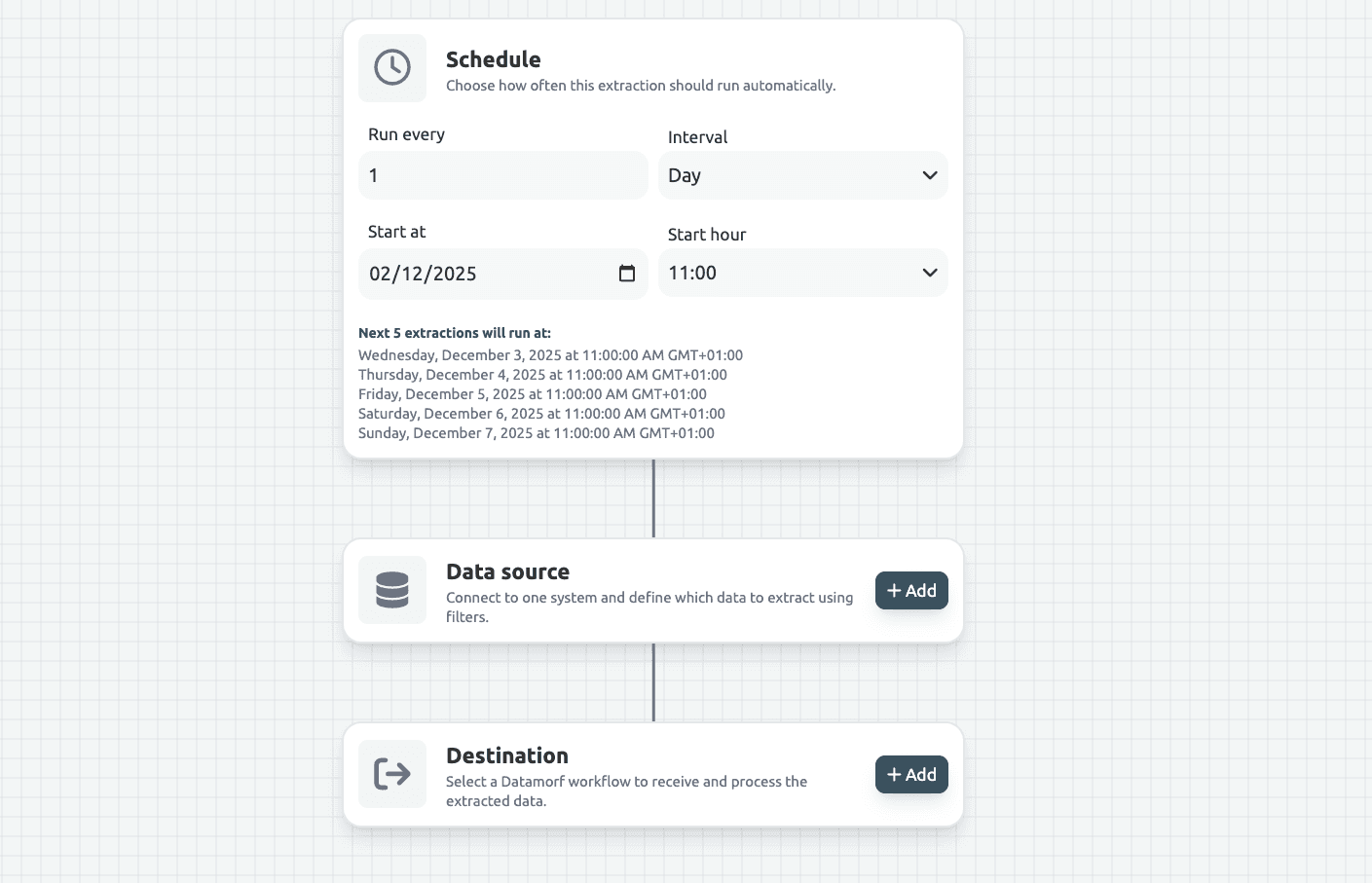
Step 1: Define the schedule
You begin by configuring how often the extraction should run.
Datamorf supports frequencies such as: hourly, every few hours, daily, weekly, or even manual-only.
The schedule acts as the trigger for the entire reverse ETL pipeline. Once activated, Datamorf executes the extraction reliably without human intervention.
Step 2: Configure the source
This is the core of the Extractor setup. You select:
the platform (CRM, database, spreadsheets, API, etc.)
the specific dataset (e.g., contacts, deals, companies, SQL query results, rows)
Datamorf then provides configuration options depending on the integration:
Filtering
You can add filters through Datamorf’s visual condition builder.
Examples:
email exists
created after 2020
status = active
Unlike workflow filters, Extractor filters only compare platform fields against constants, since workflow data does not yet exist at this stage.
Each integration has its own filtering rules, which Datamorf enforces automatically (e.g., Gmail allows only flat AND conditions, HubSpot supports OR with nested AND).
Sort
Sort allows you to specify the order in which records are fetched.
This is useful when:
you only want the newest items first,
you want stable, repeatable extraction ordering,
or you want incremental logic (e.g., oldest first).
Datamorf respects the platform’s supported sorting options and applies them automatically.
Limits & Pagination
You can optionally set extraction limits (e.g., first 100, 500, or 4000 items).
Datamorf handles pagination internally, you never need to code page walkers or API cursors.
Testing
A built-in test mode fetches the first 10 records so you can confirm the structure before running it live.
Step 3: Choose the Workflow
Once the source configuration is complete, you attach a workflow. Each extracted record (or batch) becomes its input. Datamorf offers two processing modes:
Item-by-item mode
Default: 1 request/second, 1 concurrent request
Configurable for higher throughput
Batch mode
Sends arrays up to 100 items per batch
Useful for grouped processing or bulk transformation
6. Why businesses should use Reverse ETL with Datamorf
Reverse ETL becomes significantly more powerful when paired with Datamorf because the Extractor is not a standalone tool, it is part of the full workflow engine. Businesses benefit from:
A unified automation layer
Data isn’t just extracted, it flows directly into transformations, enrichment, routing, conditional logic, and multi-destination outputs in the same environment.
Lower operational cost
Datamorf charges per workflow execution, not per row or per action. This makes reverse ETL dramatically more affordable than tools that bill by record volume.
Zero infrastructure maintenance
No cron jobs, scripts, server processes, or pagination logic. Datamorf handles concurrency, batching, retry logic, vendor rate limits, and pagination behind the scenes.
Perfect for GTM operations
Marketing, Sales, and Ops teams can refresh data daily or hourly and automatically route it to the correct systems, without engineering involvement.
Combined transform + load logic
Instead of syncing “raw” data, Datamorf lets you:
normalize fields
enrich data
standardize formats
clean invalid values
add AI processing
apply conditional routing, …
before loading into destinations.
Built for high reliability
With retries, scheduling, automatic pagination, and safe concurrency, Datamorf ensures consistent delivery even when third-party platforms have downtime.
Conclusion
Reverse ETL brings external data into your operational workflows, enabling GTM teams to work with the most up-to-date and actionable information. Datamorf’s Extractor takes this concept and makes it easy, scalable, and automation-ready.
With scheduling, filtering, sorting, batching, and native workflow integration, businesses can maintain data accuracy, automate repetitive syncs, and reduce engineering overhead, all within a predictable pricing model.
Share